Cardiac CT
What is Cardiac CT?
Cardiac CT is a new technique for diagnosing coronary artery disease.
There are 2 parts to the test:
1. Calcium Scoring:
Calcification of the coronary arteries is a sign of atherosclerotic disease. Calcium scoring is a non-contrast, low radiation dose technique (1.5-3mSv), which is quick to perform and interpret (approximately 5 minutes). This is a quicker test to perform than exercise ECG and is a more cost-effective way of diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD).
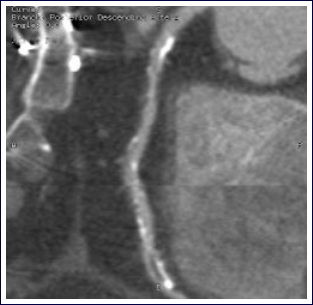
2. CT Coronary Angiography:
If your calcium score is between 1-400, you may have significant disease within your coronary arteries. To diagnose this, we perform a further CT scan with intravenous contrast to look at the blood flow within your coronary arteries.
Is Cardiac CT Reliable?
Recent studies have demonstrated both high sensitivity and specificity of cardiac computerised tomography (CCT) when compared against conventional invasive angiography for the diagnosis of significant coronary artery disease. It has also been shown to be complementary to existing non-invasive techniques. The primary value of CCT is a high negative predictive value (97-99%), making it a highly reliable investigation for ruling out significant coronary artery disease.
What do I do next?
Contact us to arrange a hospital appointment.
NICE Guidelines
NICE issued guidelines in March 2010 recommending that people with chest pain in whom stable angina cannot be diagnosed or excluded by clinical assessment alone and who have an estimated likelihood of CAD of 10-29%, should be offered calcium scoring.
Further management is then dependent on the calcium score.
Contact Us for more information

